| Basic Information | |
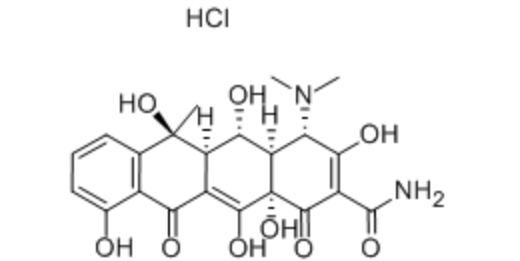
| Product name | Oxytetracycline hydrochloride |
| Grade | Feed grade/Pharma grade |
| Appearance | Yellow Crystalline powder |
| Assay | 99% |
| Shelf life | 2 Years |
| Packing | 25kg/drum |
| Condition | Keep in a cool, dry, dark location in a tightly sealed container or cylinder. |
Introduction of Oxytetracycline hydrochloride
Oxytetracycline hydrochloride is a pale yellow, bitter,crystalline compound. The amphoteric base is only slightly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. It is odorlessand stable in air but darkens on exposure to strong sunlight.The hydrochloride salt is a stable yellow powder that is more bitter than the free base. It is much more soluble in water, 1 g dissolving in 2 mL, and more soluble in alcoholthan the free base. Both compounds are inactivated rapidly by alkali hydroxides and by acid solutions below pH 2. Both forms of oxytetracycline are absorbed rapidly and equally well from the digestive tract, so the only real advantage the free base offers over the hydrochloride salt is that it is less bitter. Oxytetracycline hydrochloride is also used for parenteraladministration (intravenously and intramuscularly).
Application of Oxytetracycline hydrochloride
 Oxytetracycline hydrochloride is a salt prepared from oxytetracycline taking advantage of the basic dimethyl amino group which protonates readily to form the salt in hydrochloric acid solutions. The hydrochloride is the preferred formulation for pharmaceutical applications. Like all tetracyclines, oxytetracycline shows broad spectrum antibacterial and antiprotozoan activity and acts by binding to the 30S and 50S ribosomal sub-units, blocking protein synthesis.
Oxytetracycline hydrochloride is a salt prepared from oxytetracycline taking advantage of the basic dimethyl amino group which protonates readily to form the salt in hydrochloric acid solutions. The hydrochloride is the preferred formulation for pharmaceutical applications. Like all tetracyclines, oxytetracycline shows broad spectrum antibacterial and antiprotozoan activity and acts by binding to the 30S and 50S ribosomal sub-units, blocking protein synthesis.
Oxytetracycline is an antibiotic indicated for treatment of infections caused by Gram positive and Gram negative microorganisms such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Pasteurella pestis, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, and Diplococcus pneumoniae. It is used in studies on the oxytetracycline-resistance gene (otrA). Oxytetracycline hydrochloride is used to study phagosome- lysosome (P-L) fusion in P388D1 cells1 and antibiotic susceptibilities of Mycoplasma bovis isolates.